Exploring the Differences: CO2 vs Fiber Lasers
Exploring the Differences: CO2 vs Fiber Lasers in Industrial Applications


In the realm of industrial laser technology, two stalwarts stand out for their diverse applications and remarkable capabilities: CO2 and fiber lasers. These two laser types have revolutionized various manufacturing and fabrication processes, each with distinct strengths and specialties that cater to specific industrial needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuanced differences between CO2 and fiber lasers, dissecting their operational principles, applications, efficiency, and suitability for various materials. Whether you’re an industry professional seeking the right tool for precise cutting, engraving, or a curious enthusiast eager to understand the science behind these cutting-edge technologies, this comparison aims to shed light on their unique features and functionalities.
Join us as we navigate through the intricacies of CO2 and fiber lasers, unveiling their differences in wavelength, efficiency, speed, precision, maintenance, and overall cost-effectiveness. By the end, you’ll gain valuable insights into which laser system aligns best with specific industrial demands, ultimately aiding in informed decision-making for your manufacturing or fabrication requirements.
Let’s embark on an illuminating journey into the world of CO2 and fiber lasers, exploring their capabilities, limitations, and the industries they power with their laser precision.
- Operating Principle:
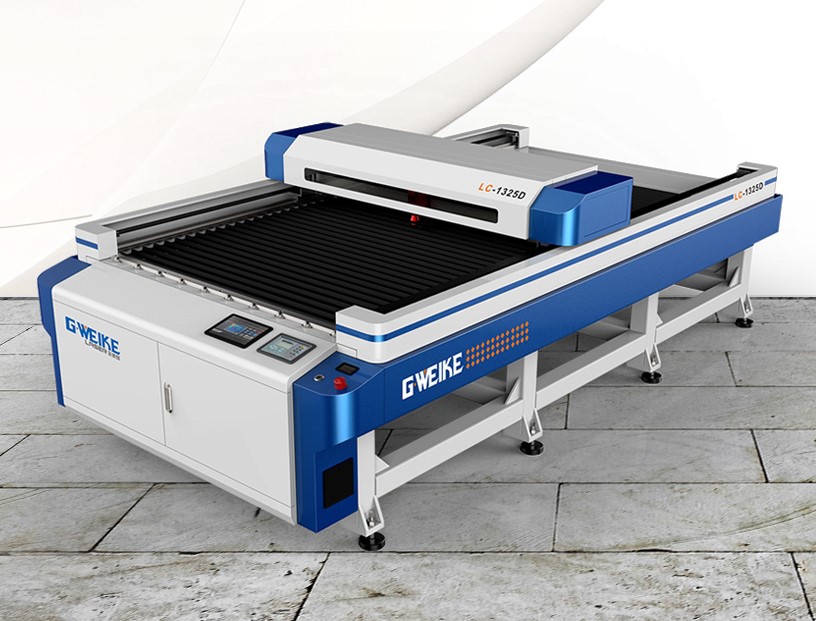
- CO2 Laser: Utilizes a gas mixture to create a laser beam by electrically stimulating the gas molecules. It emits infrared light at a wavelength of around 10.6 micrometers.
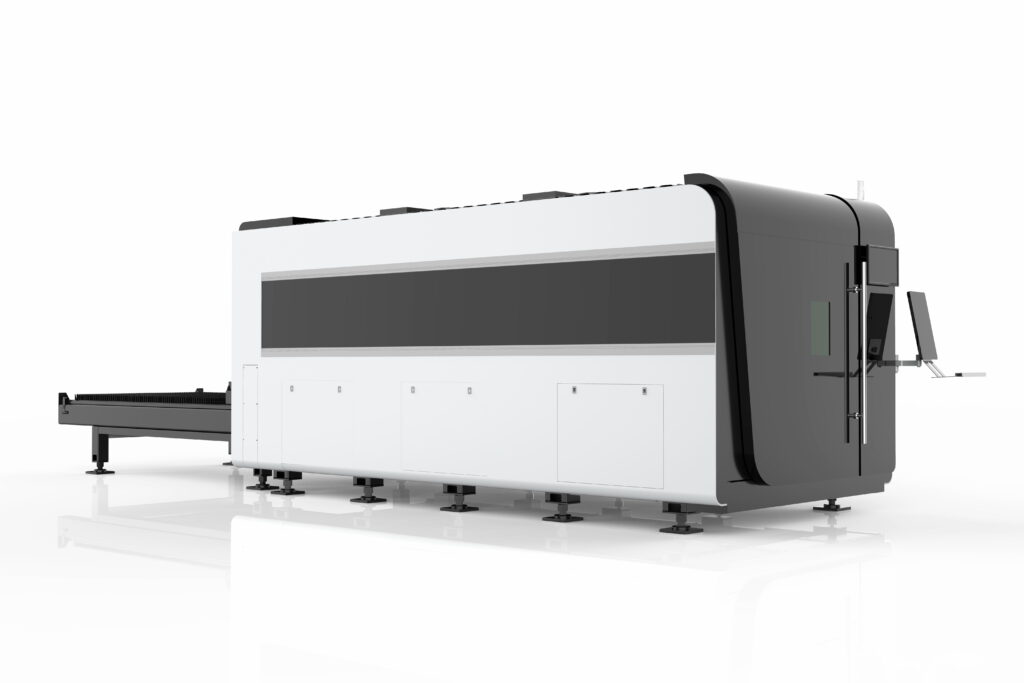
- Fiber Laser: Employs an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements like erbium, ytterbium, or neodymium to generate the laser beam. It operates in a solid-state medium and emits light typically at wavelengths ranging from 1 to 2 micrometers.
- Wavelength:
- CO2 Laser: Operates at a longer wavelength (10.6 micrometers), which is more suited for cutting or engraving non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, and some plastics.
- Fiber Laser: Emits light in a shorter wavelength range (1-2 micrometers), making it highly effective for cutting and marking various metals, including steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Efficiency and Power:
- CO2 Laser: Typically has lower wall-plug efficiency compared to fiber lasers. However, they can be powerful, suitable for thick materials and large-scale cutting jobs.
- Fiber Laser: Known for higher efficiency and can achieve higher power densities in a smaller footprint. They excel in precision cutting of thin metals.
- Maintenance and Lifespan:
- CO2 Laser: Generally requires more maintenance due to the presence of gas tubes that degrade over time. Their lifespan is shorter compared to fiber lasers.
- Fiber Laser: Offers a longer lifespan with lower maintenance requirements as they don’t have gas tubes. They are more reliable and have higher uptime.
- Speed and Precision:
- CO2 Laser: Suitable for intricate designs and fine details due to their longer wavelength, but they might not be as fast as fiber lasers in metal cutting.
- Fiber Laser: Known for high cutting speeds and superior precision, especially in metal cutting applications.
- Cost:
- CO2 Laser: Initial equipment cost can be lower compared to fiber lasers, but operational and maintenance costs might be higher in the long run due to consumables and maintenance requirements.
- Fiber Laser: Initially more expensive but offers lower operational costs and higher efficiency, making them more cost-effective over time.
- Applications:
- CO2 Laser: Ideal for engraving, cutting, and marking non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, acrylic, and some plastics.
- Fiber Laser: Well-suited for cutting, welding, engraving, and marking metals and alloys used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Choosing between CO2 and fiber lasers depends on specific application needs, material requirements, precision, budget, and operational considerations. Both types have their advantages and excel in different industrial and manufacturing settings.
Check out our range of fiber laser cutting machine below:
Sheet and tube fiber laser cutting machine